To prevent systemic hypoplasia, it is necessary:
- take care of the health of a pregnant woman and a newborn;
- engage in the prevention of infectious and non-communicable diseases in children;
- timely, qualitatively to treat the arisen diseases;
- carry out sanitary and educational work in antenatal clinics, children's institutions, constantly work in contact with pediatricians;
- to prescribe npeparat tetracycline strictly according to indications.
For the prevention of local hypoplasia, timely treatment or removal is important. baby tooth so that the inflammation from the affected milk tooth does not spread to the follicle of the permanent tooth.
Prevention of fluorosis
Fluorosis prevention consists of social and individual activities. Public events include:
- replacement of the water source;
- mixing of several water sources;
- defluorination of water (defluorination is carried out by chemical purification with alumina sulphate or by passing through bone filters). Individual prophylaxis.
Prevention of fluorosis should begin from the moment the child is born until the end of the enamel mineralization period. It is necessary for a child breast-feeding. Children are recommended a sufficient amount of milk, vitamins (B1 B6, C). Additionally, calcium gluconate is prescribed. It is recommended to brush your teeth with toothpastes that do not contain the element fluorine. The food should not contain foods that contain fluoride. It is recommended to use imported products that are produced in areas with a lower content of fluorine in water and soil.
Individual methods of preventing fluorosis include boiling drinking water, settling and drinking thawed water. In order to prevent fluorosis, it is necessary to take children out of areas where drinking water contains an excess amount of fluoride. During the school holidays, they can be taken to children's health camps, sanatoriums.
Prevention of wedge-shaped defect
In order to prevent a wedge-shaped defect, rational oral hygiene is recommended, in which teeth should be brushed with a soft brush and only toothpaste, and not tooth powder. Moreover, it is necessary to exclude horizontal movements with a brush while brushing your teeth. Recommended toothpastes: Zhemchug, Arbat, Fluorodent, Cheburashka, etc.
Prevention of tooth erosion
Prevention of tooth erosion consists of limiting the consumption of acidic foods (citrus fruits) and rational dental care. It is recommended to brush your teeth with soft brushes, use pastes containing glycerophosphate and other trace elements.
Prevention of acid necrosis
Prevention of acid necrosis lies in the proper organization of production processes. First of all, there should be sufficient supply and exhaust ventilation, automation of acid production and process sealing should be established.
All workers of chemical production should be taken to the dispensary. In the process of dispensary observation, they need to conduct courses of remineralizing therapy 2 times a year. In order to prevent the development of acid necrosis, it is necessary to install columns with alkaline water for rinsing the mouth. Workers in chemical industries should rinse their mouth after 1.5-2 hours to neutralize the resulting acid compounds in the mouth.
Author: Muravyannikova Zh.G.
Not always a change in the shape or color of the enamel is the result of exposure to microorganisms that cause caries.
In some cases, the cause of the anomaly is a non-carious lesion of the hard tissues of the teeth, which can form both in the post-follicular and follicular periods.
Classification of pathologies
Non-carious lesions of dental tissues are pathologies that are not only an aesthetic defect. They are can lead to destruction and complete loss of the tooth.
There are a variety of dental lesions of non-carious origin, which were divided into two groups depending on the moment of development of the pathology.
- The first group includes diseases that form in the period before eruption, at the phase of follicular development and the laying of rudiments, that is, during the intrauterine formation of the fetus and in infancy.
- The second group includes anomalies resulting from system failure after eruption.
Before eruption
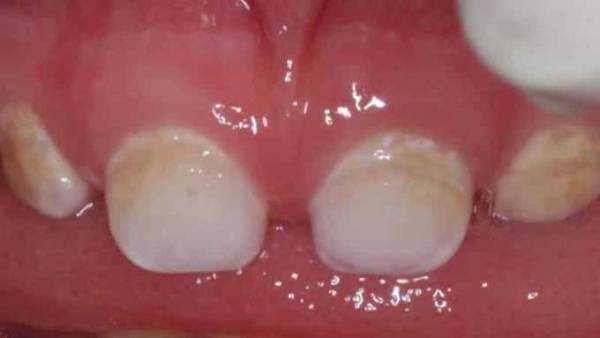 Non-carious lesions that develop before teething include:
Non-carious lesions that develop before teething include:
- Changes in the tissues of the teeth of a non-hereditary nature caused by endemic type fluorosis, impaired enamel formation (hyperplasia, hypoplasia), and resulting from exposure to toxic substances ().
- Hereditary changes in dental tissues. They include imperfect dentinogenesis, odontogenesis, amelogenesis.
This group of anomalies is characterized by the early manifestation of symptoms that can be seen on the first erupted units. They change their color and shape.
In some cases, there is a violation of the quantitative ratio of teeth in the general row, combined with their incorrect position and size.
After eruption
Pathologies that occur after eruption include:
- tooth trauma;
- increased sensitivity of enamel;
- abrasion of dental tissues;
- erosion.
This type of pathology is characterized by a change in shade and deformation of the crown part.
Prevalence and causes of development
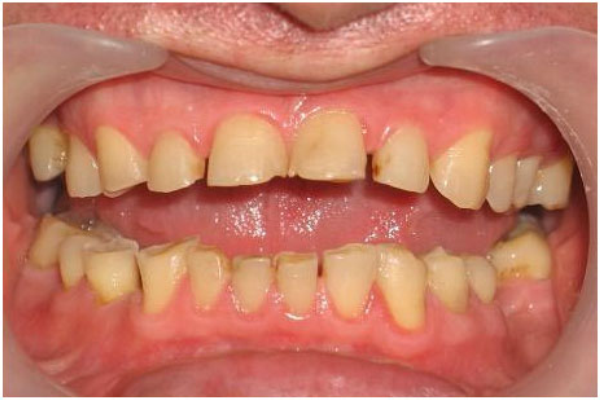
The prevalence of non-carious lesions is low. Depending on the type of pathology, it is 5–14% of all dental diseases.
The smallest part in this case falls on anomalies that develop before eruption, which do not cross the threshold of 10%. The maximum indicator refers to pathologies that occur after eruption.
The variety of non-carious pathologies makes it difficult to identify the main causes of their development. Despite modern research methods, scientists fail to come to a consensus on this issue.
Most often, the following are the reasons:
- exposure to adverse factors: genetic, chemical, physical, affecting the body of the mother or child;
- taking medications containing hormones, metals and antibacterial components;
- violation of protein and mineral metabolism, against which the metabolic process is disturbed;
- heredity.
Diagnostics
Diseases of this type require careful diagnosis, which is carried out according to a certain scheme:
- Questioning, examination and instrumental examination of the patient's oral cavity.
- Differential diagnosis, which allows you to accurately identify the form of pathology and exclude carious lesions. To do this, apply a study with the help of a probe and radiography.
- Determination of the stage and prevalence of the disease, using hardware diagnostics:,.
- Consultation with doctors from other areas: nephrologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist, gastroenterologist, geneticist, etc.
The more detailed the diagnosis is, the more accurate the treatment will be.
View overview
Each type of lesion is distinguished by its clinical manifestations and complications that can occur if left untreated.
Dysplasia and hypoplasia
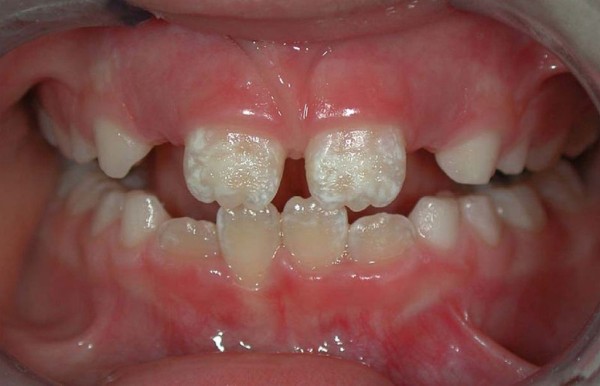 Both pathologies are characterized by similar symptoms, among which the main place is occupied by a change in the shade of enamel, its underdevelopment or complete absence, while the teeth of the same name are affected.
Both pathologies are characterized by similar symptoms, among which the main place is occupied by a change in the shade of enamel, its underdevelopment or complete absence, while the teeth of the same name are affected.
The disease manifests itself as white chalky or brown spots with a striated or deepened glossy surface that reacts to irritants only in the absence of enamel.
Often these teeth have an abnormal barrel or awl shape. Without appropriate treatment, it contributes to the formation of malocclusion and affects deep tissues, leading to their destruction.
Hyperplasia
It is characterized by excessive formation of enamel and dentin, which appear on the surface of the tooth in the form of a drop, up to 4 mm in diameter. Most often, it is localized at the border of cement and enamel, and in the neck area.
With a large diameter, the formation can interfere with the quality of chewing food. Otherwise, hyperplasia acts only as an aesthetic defect and does not have serious consequences.
hereditary lesions
Hereditary lesions can involve enamel and dentin, causing their hypoplasia. Pathologies are manifested by the irregular shape of the teeth, abnormal color, size and relief of the enamel.
Hereditary anomalies in some cases do not develop beyond a minimal change in the color of the enamel, being an aesthetic defect. But in other situations, they lead to tooth decay.
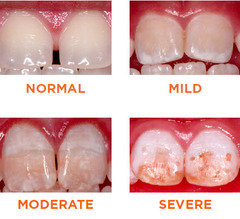
Fluorosis
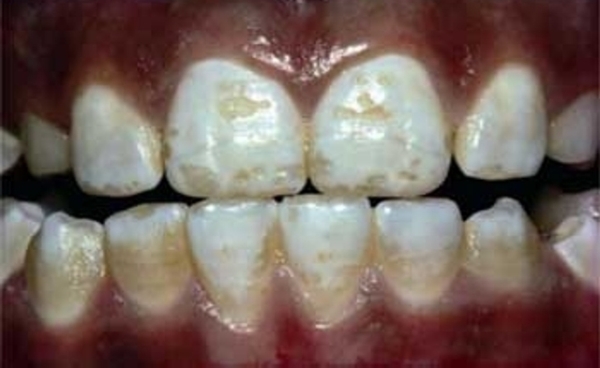 It is a disease characterized by a depigmented light white matte unit, the surface of which is covered with erosions without enamel. With advanced forms, tooth spalls and the spread of the disease to the bone tissue of the skeleton are observed.
It is a disease characterized by a depigmented light white matte unit, the surface of which is covered with erosions without enamel. With advanced forms, tooth spalls and the spread of the disease to the bone tissue of the skeleton are observed.
More details about this pathology are described in the following video:
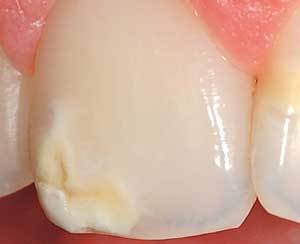
Erosions and wedge-shaped defect
They are among the most common pathologies of non-carious origin. Erosions occur with neglected forms of various non-carious lesions.
One of the variants of manifestations is a wedge-shaped defect, which is formed in the area of the neck of the tooth. With the growth of erosion, severe pain occurs, and with its deepening, a tooth can break off.
Hyperesthesia
It is manifested by a pronounced sensitivity of the enamel to external stimuli, with a sharp onset of pain at the time of exposure. IN initial stage pathology is manifested by constant soreness and discomfort when using cold, sour, salty.
It complicates the process of cleaning the dentition, which provokes the occurrence of multiple bacterial plaque and the development of caries.
hard tissue necrosis
Pathology is characterized by multiple destruction of dental tissues in the form of small cavities with uneven boundaries and a changed shade.
The affected tooth reacts to irritating factors with sharp severe pain. Further growth of damage leads to its abrasion in the vertical or horizontal direction.
Mechanical injury
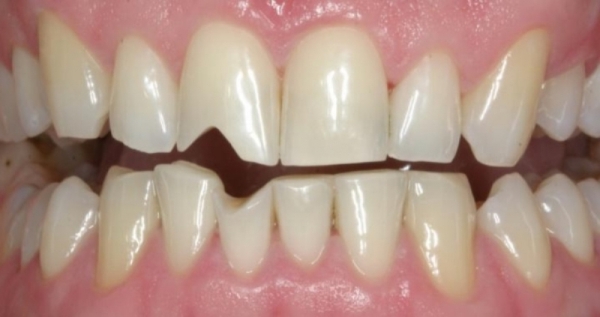 Tooth injuries include cracks in dental tissues, bruises, fractures of the root and crown parts, dislocation or damage to the rudiment. The clinical picture will depend on the type of injury, but most often they are manifested by soreness, tooth mobility and chewing dysfunction.
Tooth injuries include cracks in dental tissues, bruises, fractures of the root and crown parts, dislocation or damage to the rudiment. The clinical picture will depend on the type of injury, but most often they are manifested by soreness, tooth mobility and chewing dysfunction.
In the absence of specialized dental care, the consequence of trauma in most cases is tooth loss.
Principles and methods of treatment
For each type of non-carious lesion, a certain type of treatment is used, but at the same time, all the methods used are built on the basis of certain principles:
- Complexity. Treatment should include both local and general remineralizing therapy, which will help restore the structure of dental tissues.
- Subsequence. If necessary, treatment should be continued with the restoration of teeth, supporting remineralizing and restorative therapy.
Treatment should be carried out against the background of dietary adjustments and improving the quality of oral hygiene.
Remineralization
It is the main treatment option for all types of non-carious lesions, as it clogs the enlarged pores of dental tissues and restores their structure.
Remineralizing therapy includes phosphorus-calcium preparations prescribed for both general and local use. General therapy is carried out by a course lasting 1 month with regular repetition at least 2 times during the year.
For administration, calcium glycerophosphate is used with a dosage for a certain age. At the same time, vitamin complexes are prescribed, for example, Kvadevit or Complevit.
In the dental office, professional remineralization is carried out using fluorine-containing varnishes, gels or sodium fluoride solution. If necessary, deep fluorination is carried out with a two-phase agent, which includes copper, fluorine, calcium hydroxide.
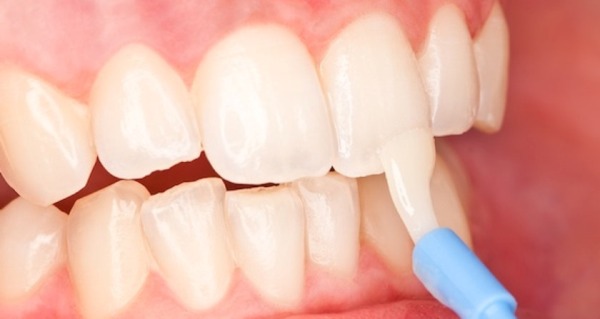
Also, daily applications with phosphate-containing toothpastes are applied to the dentition, lasting from 5 to 15 minutes. It is recommended to repeat this procedure twice a day.
To enhance the effect of remineralization, electrophoresis with calcium glycerophosphate can be prescribed.
Load reduction
An important factor in the treatment of non-carious lesions is elimination of factors that increase the load on the tooth. In their capacity, most often teeth are antagonists of another jaw or dental structures.
To reduce the load, they resort to grinding the contact surface of interlocking units or existing seals. If the bite is significantly lowered, then it is built up.
In the absence of teeth, prosthetics are recommended, which will ensure an even distribution of the load. Taking into account the overload factor, in most cases, reduces the intensity of the progression of the pathology or stops its further spread.
filling
One of the main stages of treatment is the restoration of the crown part of the teeth with the help of filling. Restoration is not recommended during the acute period of the disease, as there is a high probability of rejection of the filling.
In case of severe painful manifestations, a filling using a temporary composite is allowed. In this case, only gentle preparation with minimal tissue grinding is allowed.
The most optimal time for restoration is the period of remission. Glass ionomer materials are used to restore small surface deformations.
Volumetric lesions are covered with a combination of materials, where the basis is glass ionomer, and the top layer is laid composite.
Implantation
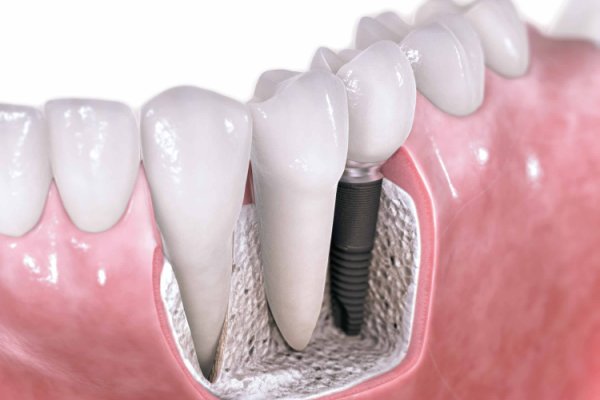 Implantation is resorted to in case of violation of the integrity of a row of teeth in order to reduce the load, as well as in the event of non-carious lesions against the background of osteoporosis. In both cases, implants will not only restore the dentition, but also all its functions.
Implantation is resorted to in case of violation of the integrity of a row of teeth in order to reduce the load, as well as in the event of non-carious lesions against the background of osteoporosis. In both cases, implants will not only restore the dentition, but also all its functions.
This has a beneficial effect on the work of many body systems, which improves the quality of life of the patient.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
In addition to caries, there are a huge number of dental diseases. One of the most common pathologies is non-carious lesions of the enamel. Some of them have already been well studied in terms of symptoms, but some have not yet been finally sorted out. In this article, we will consider such a pathology as enamel hyperplasia. The development of such a pathology occurs in the process of laying and forming teeth in children.
What is enamel hyperplasia
The main manifestation of the disease is non-carious changes in the appearance of the tooth.
During the formation of teeth in children with this pathology, its excess is formed, which manifests itself in the form of whitish convex islands. The overall functionality of the tooth remains normal, the disease does not cause any discomfort.
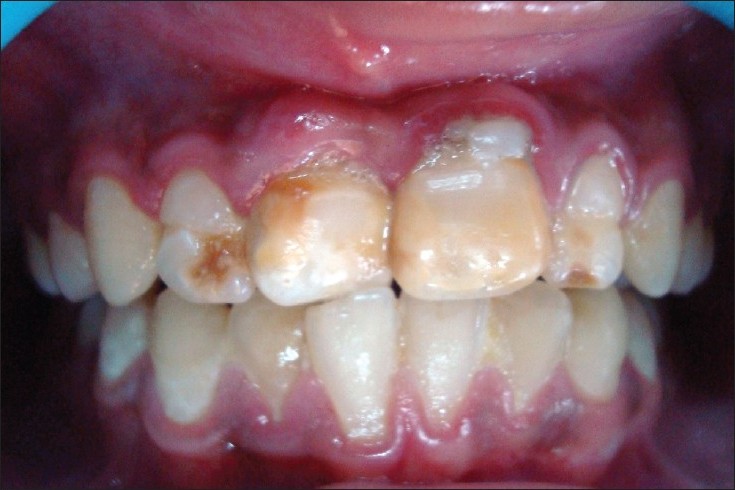
Growths on the teeth - hyperplasia
It should be noted that this damage to the dental tissue is in no way associated with softening of the enamel with the participation of microorganisms. Hyperplasia is based on a violation of tooth mineralization under the influence of not only internal, but also external factors. In the presence of such a disease, even after its detection, only a third of all seek advice and help from a dentist.
General information and structure of enamel drops
Hyperplasia is a condition where excess tissue forms on the surface of a tooth. Pathology can develop both on milk and already on new teeth of a permanent nature.
Most often, the processes are formed in the basal part of the tooth or in the area of \u200b\u200broot growth. Hyperplasia or enamel drops are small in size from 1 mm, but in some rare cases they can reach up to 5 mm. Such a violation is diagnosed in almost 2% of the world's population.
The only problem in diagnosing this deviation is an asymptomatic course.
The development of such small processes very often proceeds without any pain and therefore does not cause concern and desire to see a doctor. Most often, the problem is an unaesthetic appearance, especially if the problem is focused on the front teeth.
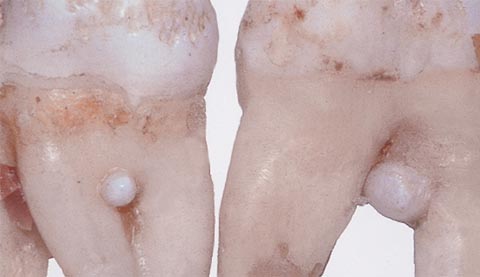
Enamel drops on torn teeth
Dentists strongly recommend that if any deviations are found, even those that do not bring discomfort at the initial stage of development, seek advice and professional examination. It is better to remove cervical hyperplasia at the initial stage, because in practice it happens that such formations provoke the development of inflammatory processes in the gums.
Several types of enamel drops are determined by location:
- root;
- cervical;
- coronal.
By structure, hyperplasia is classified into:
- true enamel;
- enamel-dentine drops;
- enamel-dentine drops with cavities inside filled with pulp;
- drops of Rodriguez-Ponti, which are located in the periodontium in the form of nodular formations;
- drops are intradentinal, which are embedded in the dentin of the crown or the tooth itself.
Enamel drops on the edge of the tooth
Enamel drops that form in the dentin of the tooth cannot be diagnosed visually. Most often they can be found in the process of treating a tooth affected by caries. The bur machine accidentally hits a hardened area of dentin. Cervical hyperplasia is visible when probing the gums, and root hyperplasia can only be detected by the results of an X-ray examination.
You can treat only drops of enamel, which are located near the neck of the tooth.
The treatment process consists in polishing the tissue area with a diamond burr and subsequent daily care in the form of applications of fluoride-containing toothpaste. Treatment continues for a week or 10 days on the recommendation of the attending physician.
Preventive measures to prevent the appearance of hyperplasia
Prevention of the development of dental hyperplasia in children consists in measures to prevent caries during the growth of milk teeth. It is also important to deal with complications that interfere with the normal formation of already permanent teeth. Every six months, take your child to the dentist to monitor the dynamics of tooth growth and conduct a professional cleaning of the oral cavity.
Hyperplasia in advanced form
You can also try such a procedure as fissure sealing with composite material and a remineralization procedure.
Such activities will reduce the risk of developing any kind of enamel hyperplasia, and the baby's teeth will grow strong and radiate health.
To protect both an adult and a child from every adverse factor is simply an impossible task, therefore the main optimal way to combat the development of caries, hyperplasia, periodontitis and other maxillofacial problems is constant medical supervision. Starting with a woman who is preparing to become a mother, and then her child. The expectant mother is registered and observed from the 8th week of pregnancy and the observation continues until the child reaches the age of two years. After that, the child is simply taken for a routine examination to a pediatric dentist.
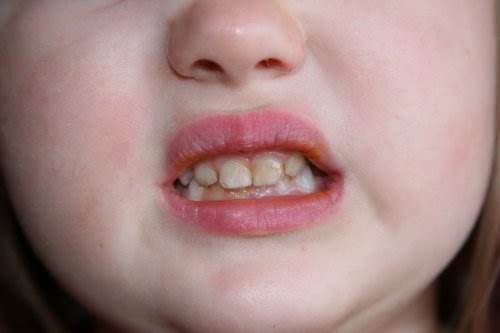
Hyperplasia in a child - the initial stage
If the pregnancy is easy and the woman is not worried about problems with her teeth, then she must definitely visit the dentist 4 times. At the eighth, eighteenth, twenty-eighth and thirty-eighth weeks. The task of the dentist is to identify caries at an early stage of its development or periodontitis. To acquaint a woman with preventive measures for caring for her teeth and the entire oral cavity, to teach a mandatory set of skills in individual hygiene. If diseases of the oral cavity are detected during pregnancy, then the number of visits to the dentist is prescribed on an individual basis and allows you to adjust the treatment until the expectant mother fully recovers.
If the baby does not have problems with the oral cavity, then a dentist consultation is needed no more than once a year (up to three years). Then a dentist consultation is required every 6 months. When diagnosing tooth enamel hyperplasia, observation flows into the treatment process, which lasts until the teeth are completely cured.
Reasons for the development of hyperplasia
Very often, such a deviation from the norm as hyperplasia is observed in connection with hormonal disruptions in organism. Such a cup most often ripens during puberty, during childbearing, with certain blood diseases and an excess of formed tartar. Sometimes the appearance of pearl drops is provoked by malocclusion, which injures the surface of the tooth enamel. However, the main reason is the insufficient amount of fluoride in the tooth enamel or its excessive supply.
Forms of enamel hyperplasia
Treatment process
With the help of a drill, it is possible to cure cervical hyperplasia, which, in the process of growth and development, can provoke inflammation of the gums. Tooth drops are removed, after which the enamel is polished. Further, the dentist individually prescribes complex therapy with drugs.
If a child is afraid of a doctor, then before going to a consultation, the baby should be prepared and told about the beauty of even and white teeth. He must understand that teeth are needed not only to eat, but also for beauty, to smile and everyone around him could see how beautiful and healthy his teeth are. If there are uneven teeth in the mouth, then this is reflected in the pronunciation of words, in the bite and even in the shape of the face, which does not really decorate the guys. That is why you need to constantly go to the dentist, who helps all children to have beautiful teeth.
Enamel sealant is used in the treatment
The treatment process depends on the type of violation and the characteristics of dental pearls.
Another very important point is when the patient asked for help, namely, how advanced the disease is. Modern medical centers and innovative equipment allow treatment to be absolutely painless with minimal time and financial costs. Today you can get rid of hyperplasia quickly and efficiently. Sometimes the attending physician recommends additional orthodontic treatment. You may need, in addition to applications with fluorine and calcium, electrophoresis with calcium ions.
A good specialist will be able to diagnose hyperplasia at an early stage of its development, which will facilitate the treatment process and relieve gum problems.
It is important not only to identify the symptoms of the disease and prescribe effective treatment, but also to understand the root causes of the development of the anomaly in order to exclude them.
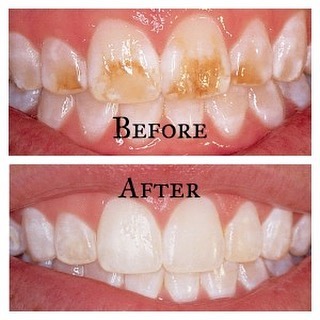
Unfortunately, even after successful treatment, light spots on the enamel sometimes remain and such defects can be eliminated only through microprosthetics. But such a procedure is performed by a dentist, only for persons who have reached the age of majority, so all childhood will have to go through with unaesthetic defects on the teeth.
Treatment of timely detected hyperplasia
Important right from the start early age teach the child to properly care for their teeth and the entire oral cavity, so that in the future they will not lose permanent teeth ahead of time. It is recommended to start caring for the child's oral cavity from the very moment of his birth, even despite the fact of the absence of teeth. Often, after breastfeeding, bacteria accumulate in the baby's mouth, which lead to inflammatory processes on the mucous membrane. Young parents should monitor this and regularly wipe the child's gums with a soft cloth dipped in warm water or with a gauze swab.
Not only permanent teeth, but also milk teeth need careful care.
Because the correct laying and formation of permanent teeth depends on the condition of milk teeth, and diseases on temporary teeth can lead to deformations, unaesthetic problems.
It would be good if all parents understood that with the appearance of the first tooth in a baby, he needs to purchase his own brush, toothpaste and learn how to handle them. The main thing is to carefully approach the choice of products that will not harm the child.
- a group of diseases, the occurrence of which is not associated with the influence of a microbial factor. The main complaints are reduced to the appearance of an aesthetic defect. Rarely, hyperesthesia occurs. Non-carious lesions of the teeth are accompanied by destruction of hard tissues. Diagnosis is based on complaints, anamnesis of the disease, clinical examination data and the results of additional research methods. Treatment of non-carious lesions of the teeth is aimed at restoring the mineral composition of hard tissues, eliminating the aesthetic defect, and normalizing the chewing function.
With non-carious lesions of the teeth of a hereditary nature, prosthetics are indicated to preserve hard tissues. Fluorosis patients are advised to limit their intake of fluoride-rich foods. Inside prescribe calcium-containing drugs. Fluorescent spots are subject to grinding with subsequent restoration of teeth with composites, ceramic crowns and veneers. To eliminate pigmentation, combined (external and intracanal) bleaching is carried out. The prognosis for non-carious lesions of the teeth is determined both by the nature of the pathology and the time of occurrence, as well as the timeliness of the patient's visit to a medical institution, as well as the level of treatment.
Caries with all its accompanying complications is the undisputed leader among dental diseases. Approximately 90% of visits to dentists are associated with carious processes. Non-carious lesions of the hard tissues of the tooth are much less common, but cause no less trouble. The pathogenesis of some non-carious lesions has not been fully elucidated, it is only indisputable that defects are formed without the participation of pathogenic microflora. However, bacteria join the process of tooth decay with great pleasure, and the already existing pathological process is aggravated by caries.
Prices for the treatment of non-carious lesions
Treatment of non-carious lesions of tooth tissues 4032 P
Specialists in the treatment of non-carious lesions

Litvin Irina Borisovna
doctor of the highest category dentist-therapist1991 - graduated from the Moscow State University of Medicine and Dentistry. Semashko specializing in dentistry.
1991-1992 - passed a clinical internship on the basis of the Zelenograd city polyclinic, specializing in therapeutic dentistry.
1995 - graduated from advanced training courses at the faculty of advanced training of dentists of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
Non-carious lesions of hard dental tissues are divided into two groups:
- Arising at the stage of development of dental germs;
- Developing teething field.
The first group includes fluorosis, enamel hyperplasia, local and systemic hypoplasia, anomalies in the structure and development of the dentition. Some diseases are genetically determined, some are due to adverse effects on the rudiments of teeth during fetal development or in early childhood. Such unfavorable factors include mother's illness during pregnancy, the intake of certain drugs, and the peculiarities of the ecological situation in the region. After eruption, under the influence of chemical, mechanical and other environmental factors, erosion and wedge-shaped enamel defects, necrosis, hyperesthesia, and pathological abrasion of teeth may develop. This group also includes injuries.
The classification according to ICD-S, developed on the basis of ICD-10, looks a little different. Due to radically different mechanisms of pathogenesis, anomalies in the development of teeth and actually non-carious tissue lesions belong to different groups. The most common non-carious lesions of the teeth Hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the enamel. Enamel hypoplasia can be local or systemic. Systemic hypoplasia is a consequence of metabolic disorders of proteins and mineral salts, local - against the background of certain diseases and an inadequate diet. Sometimes enamel hypoplasia has a traumatic origin. The defect looks like cup-shaped spots or grooves on the surface of the tooth. Occasionally there is a complete absence of the enamel layer - aplasia. In our clinic, the defect is corrected by the method of microprosthetics.
A few videos about non-carious lesions of the teeth
The main types of non-carious lesions of the teeth
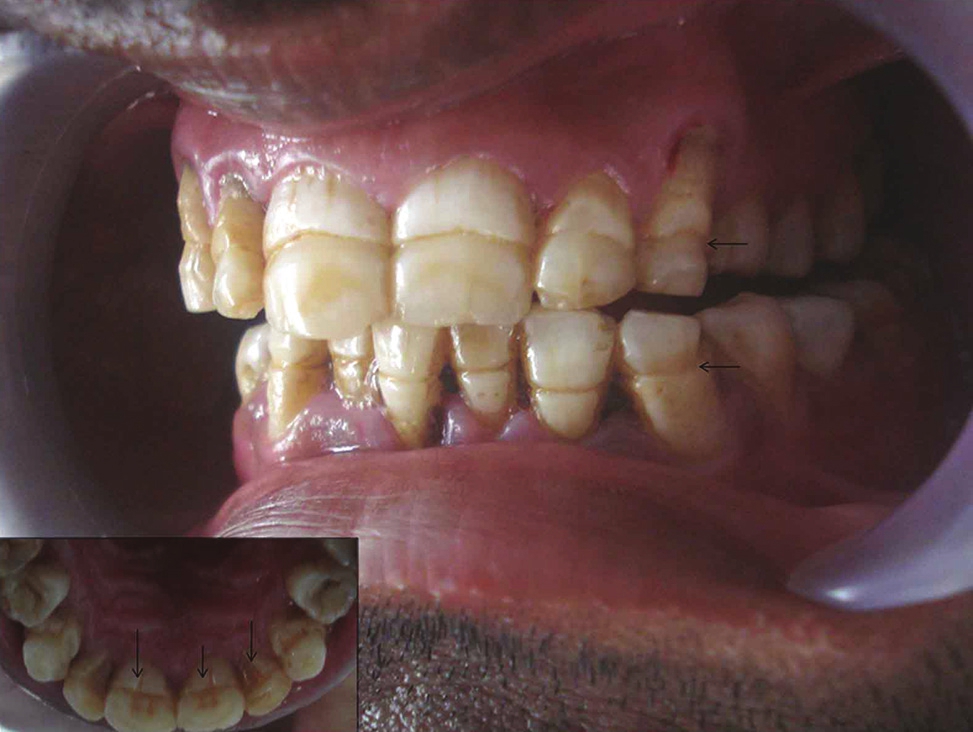
Photos with examples of non-carious lesions
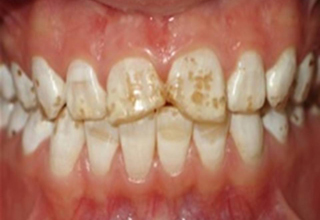
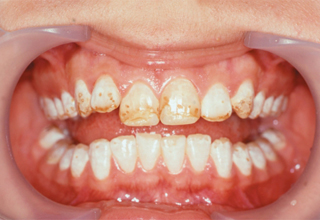
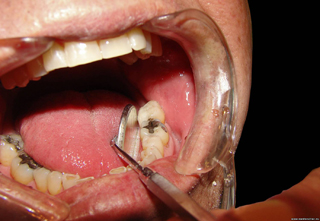
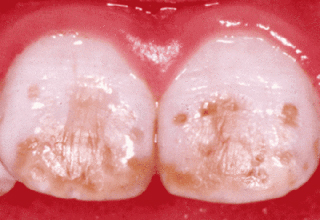
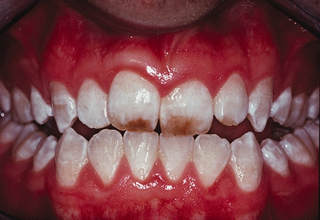
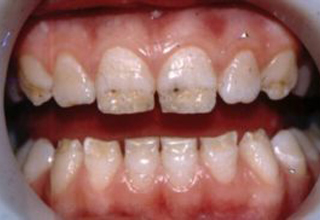
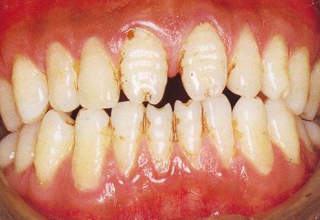
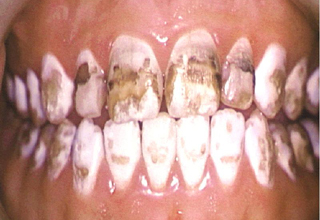
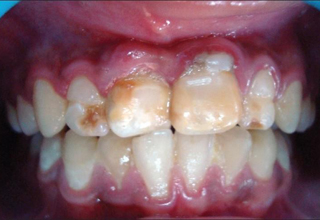
In the photo, necrotic lesions, wedge-shaped defects and erosion look very similar, only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. The ICD-10 classification also includes other pathologies of hard tissues of the tooth, but many of them are extremely rare. The cost of treating a specific defect is calculated on an individual basis, taking into account the prices of materials and the volume of intervention.
